Overview
What Is Retinopathy?
Retinopathy Is The Name Given To 'Disease Of The Retina' Due To Diabetes, And Is Described Below. Blindness From Retinopathy Can In Theory Be Prevented, And Has In Iceland. This Has Been Done By Regular Eye Checks And People Controlling Their Diabetes.Types Of Retinopathy
There Are Four Main Types Of Retinal Damage That Can Occur If You Are Diabetic. Unfortunately The Condition May Progress From No Or Mild Retinopathy To A Much More Severe Type.- No Retinopathy…. Many People Have A Basically Healthy Retina. If You Can Control Your Diabetes And Blood Pressure At This Stage It Will Help Prevent Or Slow Down Any Harmful Changes.
- Background Retinopathy …. Early Changes.
- Maculopathy ….This Is More Serious. Eventually Your Sight May Become Reduced. Laser And Blood Pressure Control Help.
- Pre-Proliferative Or Non-Proliferative Stage Before The New Blood Vessels Start Growing.
- Proliferative Retinopathy … When The New Vessels Grow. These Blood Vessels Are Very Delicate And Can Bleed Easily. Laser Is Very Effective In Stopping The New Vessels Grow.
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy?
Changes In Blood-Sugar Levels Increase Your Risk Of Diabetic Retinopathy, As Does Long-Term Diabetes. Generally, Diabetics Don't Develop Diabetic Retinopathy Until They Have Had Diabetes For At Least 10 Years, But It Is Not Wise To Wait That Long To Have An Eye Exam. As Soon As You've Been Diagnosed With Diabetes, You Need To Have A Dilated Eye Exam At Least Once A Year.
High Blood Sugar Can Damage Blood Vessels In The Retina, And When They Are Damaged, They Can Leak Fluid Or Bleed. This Causes The Retina To Swell And Form Deposits. This Is An Early Form Of Diabetic Retinopathy Called Nonproliferative Or Background Retinopathy.
In A Later Stage, Called Proliferative Retinopathy, New Blood Vessels Grow On The Surface Of The Retina. These New Blood Vessels Can Lead To Serious Vision Problems Because They Can Break And Bleed Into The Vitreous, The Clear, Jelly-Like Substance That Fills The Center Of The Eye. Proliferative Retinopathy Is A Much More Serious Form Of The Disease And Can Lead To Blindness.
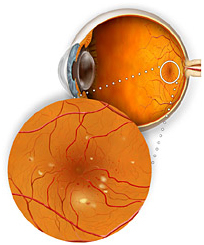 |
 |
|---|
Top: Background Diabetic Retinopathy Is An Early Sign Of Damage To The Retina At The Back Of The Eye, Where Blood Vessels Begin To Weaken And Leak. The Leakage Causes Accumulations Of Yellowish Proteins And Fatty Substances. Bottom: In The Late Stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy, You May Have Blind Spots And/Or Floaters.
Fortunately, You Can Significantly Reduce Your Risk Of Developing Diabetic Retinopathy By Using Common Sense And Taking Good Care Of Yourself.
- Keep Your Blood Sugar Under Good Control.
- Monitor Your Blood Pressure And Keep It Under Good Control, Or Seek Appropriate Care.
- Maintain A Healthy Diet.
- Exercise Regularly.
- Follow Your Doctor's Instructions To The Letter.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes Is A Condition Where The Body Does Not Produce Enough Insulin, Or Is Unable To Use Insulin Properly. Insulin Is A Hormone That Helps To Break Down Glucose (Sugar) So That It Can Be Used By The Body’s Cells As Fuel.
Due To The Problem With Making And/Or Using Insulin, The Level Of Glucose In The Blood Rises. This Increase Can Cause A Wide Range Of Complications, Such As Diabetic Retinopathy.
There Are Two Types Of Diabetes That Are Described Below.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes Is Where The Body Does Not Produce Any Insulin. The Condition Usually Begins In People Who Are Under 40 Years Of Age, Often Developing During The Teenage Years. People With Type 1 Diabetes Will Require Injections Of Insulin For The Rest Of Their Life.Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Is Where The Body Does Not Produce Enough Insulin To Be Able To Function Properly, Or Where The Body’s Cells Do Not React To Insulin. Being Overweight Or Obese Is A Major Risk Factor For Type 2 Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes Can Develop At Any Age, But Usually Affects People Who Are 45 Years Of Age Or Over. Some People With Type 2 Diabetes Can Control Their Symptoms Using A Combination Of Diet And Exercise. More Serious Cases Require Insulin Injections.Symptoms
Symptoms Of Diabetic Retinopathy Include: -- Seeing Spots Or Floaters In Your Field Of Vision
- Blurred Vision
- Having A Dark Or Empty Spot In The Center Of Your Vision
- Difficulty Seeing Well At Night
In Patients With Diabetes, Prolonged Periods Of High Blood Sugar Can Lead To The Accumulation Of Fluid In The Lens Inside The Eye That Controls Eye Focusing. This Changes The Curvature Of The Lens And Results In The Development Of Symptoms Of Blurred Vision. The Blurring Of Distance Vision As A Result Of Lens Swelling Will Subside Once The Blood Sugar Levels Are Brought Under Control. Better Control Of Blood Sugar Levels In Patients With Diabetes Also Slows The Onset And Progression Of Diabetic Retinopathy.
Often There Are No Visual Symptoms In The Early Stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy. That Is Why The American Optometric Association Recommends That Everyone With Diabetes Have A Comprehensive Dilated Eye Examination Once A Year. Early Detection And Treatment Can Limit The Potential For Significant Vision Loss From Diabetic Retinopathy.
Diabetic Retinopathy Is The Result Of Damage Caused By Diabetes To The Small Blood Vessels Located In The Retina. Blood Vessels Damaged From Diabetic Retinopathy Can Cause Vision Loss : -
- Fluid Can Leak Into The Macula, The Area Of The Retina Which Is Responsible For Clear Central Vision. Although Small, The Macula Is The Part Of The Retina That Allows Us To See Colors And Fine Detail. The Fluid Causes The Macula To Swell, Resulting In Blurred Vision.
- In An Attempt To Improve Blood Circulation In The Retina, New Blood Vessels May Form On Its Surface. These Fragile, Abnormal Blood Vessels Can Leak Blood Into The Back Of The Eye And Block Vision.
Diabetic Retinopathy Is Classified Into Two Types : -
- Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) Is The Early State Of The Disease In Which Symptoms Will Be Mild Or Non-Existent. In NPDR, The Blood Vessels In The Retina Are Weakened Causing Tiny Bulges Called Microanuerysms To Protrude From Their Walls. The Microanuerysms May Leak Fluid Into The Retina, Which May Lead To Swelling Of The Macula.
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Is The More Advanced Form Of The Disease. At This Stage, Circulation Problems Cause The Retina To Become Oxygen Deprived. As A Result New Fragile Blood Vessels Can Begin To Grow In The Retina And Into The Vitreous, The Gel-Like Fluid That Fills The Back Of The Eye. The New Blood Vessel May Leak Blood Into The Vitreous, Clouding Vision.
Other Complications Of PDR Include Detachment Of The Retina Due To Scar Tissue Formation And The Development Of Glaucoma. Glaucoma Is An Eye Disease Defined As Progressive Damage To The Optic Nerve. In Cases Of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy, The Cause Of This Nerve Damage Is Due To Extremely High Pressure In The Eye. If Left Untreated, Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Can Cause Severe Vision Loss And Even Blindness.
Risk Factors For Diabetic Retinopathy Include : -
- Diabetes — People With Type 1 Or Type 2 Diabetes Are At Risk For The Development Of Diabetic Retinopathy. The Longer A Person Has Diabetes, The More Likely They Are To Develop Diabetic Retinopathy, Particularly If The Diabetes Is Poorly Controlled.
- Race — Hispanic And African Americans Are At Greater Risk For Developing Diabetic Retinopathy.
- Medical Conditions — Persons With Other Medical Conditions Such As High Blood Pressure And High Cholesterol Are At Greater Risk.
- Pregnancy — Pregnant Women Face A Higher Risk For Developing Diabetes And Diabetic Retinopathy. If Gestational Diabetes Develops, The Patient Is At Much Higher Risk Of Developing Diabetes As They Age.
How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
Diabetic Retinopathy Can Be Diagnosed Through A Comprehensive Eye Examination.
Diabetic Retinopathy Can Be Diagnosed Through A Comprehensive Eye Examination. Testing, With Special Emphasis On Evaluation Of The Retina And Macula, May Include:
- Patient History To Determine Vision Difficulties Experienced By The Patient, Presence Of Diabetes, And Other General Health Concerns That May Be Affecting Vision
- Visual Acuity Measurements To Determine The Extent To Which Central Vision Has Been Affected
- Refraction To Determine The Need For Changes In An Eyeglass Prescription
- Evaluation Of The Ocular Structures, Including The Evaluation Of The Retina Through A Dilated Pupil
- Measurement Of The Pressure Within The Eye
Supplemental Testing May Include:
- Retinal Photography Or Tomography To Document Current Status Of The Retina
- Fluorescein Angiography To Evaluate Abnormal Blood Vessel Growth
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
According To The American Academy Of Ophthalmology, 95 Percent Of Those With Significant Diabetic Retinopathy Can Avoid Substantial Vision Loss If They Are Treated In Time. The Possibility Of Early Detection Is Why It Is So Important For Diabetics To Have A Dilated Eye Exam At Least Once A Year.Diabetic Retinopathy Can Be Treated With Laser Photocoagulation To Seal Off Leaking Blood Vessels And Destroy New Growth. Laser Photocoagulation Doesn't Cause Pain, Because The Retina Does Not Contain Nerve Endings.
In Some Patients, Blood Leaks Into The Vitreous Humor And Clouds Vision. The Eye Doctor May Choose To Simply Wait To See If The Clouding Will Dissipate On Its Own, A Period Called "Watchful Waiting." A Procedure Called A Vitrectomy Removes Blood That Has Leaked Into The Vitreous Humor. The Body Gradually Replaces Lost Vitreous Humor, And Vision Usually Improves.
If Diabetic Retinopathy Has Caused Your Body To Form A Cataract, It Can Be Corrected Surgically. Patients Who Have Developed Glaucoma Should See A Glaucoma Specialist.
For more information, medical assessment and medical quote
as email attachment to
Email : - info@wecareindia.com
Contact Center Tel. (+91) 9029304141 (10 am. To 8 pm. IST)
(Only for international patients seeking treatment in India)










