Overview
Dental Extraction OR "Pulling Teeth"
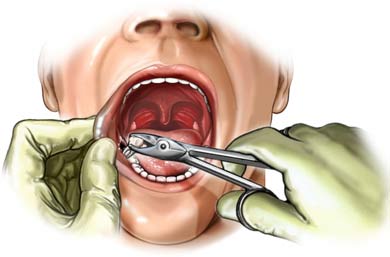 Sometimes anaolgies are made with reference to "pulling teeth". People might say getting their childern to eat vegetables is like "pulling teeth". We believe the reason is that "pulling teeth" is never fun or easy.
Sometimes anaolgies are made with reference to "pulling teeth". People might say getting their childern to eat vegetables is like "pulling teeth". We believe the reason is that "pulling teeth" is never fun or easy. A dental extraction is the removal of a tooth from the mouth. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons. Tooth decay that has destroyed enough tooth structure to prevent restoration is the most frequent indication for extraction of teeth. Extractions of impacted or problematic wisdom teeth are routinely performed, as are extractions of some permanent teeth to make space for orthodontic treatment.
Historically, dental extractions have been used to treat a variety of illnesses, as well as a method of torture to obtain forced confessions. Before the discovery of antibiotics, chronic tooth infections were often linked to a variety of health problems, and therefore removal of a diseased tooth was a common treatment for various medical conditions. Instruments used for dental extractions date back several centuries. As dental extractions can vary tremendously in difficulty, depending on the patient and the tooth, a wide variety of instruments exist to address specific situations.
Reasons For Tooth Extraction
The most common reason for extracting a tooth is tooth damage such as breakage or fracture.
Some other possible reasons for tooth extraction are as follows : -
- Extra teeth which are blocking other teeth from coming in.
- Severe gum disease which may affect the supporting tissues and bone structures of teeth.
- Severe tooth decay, caries or infection.
- In preparation for orthodontic treatment (braces)
- Insufficient space for wisdom teeth (impacted wisdom teeth).
- Receiving radiation to the head and neck may require extraction of teeth in the field of radiation.
Surgical Or Nonsurgical Extractions
Dental extractions are classified as "simple" (non-surgical) or surgical. Dr. Hale, a friend, collegue and fellow veterinary dental consultant has stated; "dental extraction can be awfully simple or simply awful". We find with appropriate training, equipment, instruments and skill, there are far fewer "awful" extraction experiences.
Taking dental radiographs and carefully evaluating them is the mandatory first step in our practice for every dental procedure. This helps identify potential problems that may occur especially with dental extractions. Problems such as tooth ankylosis, tooth resorption or root dilaceration (curved roots) create unique challanges and may require special surgical technique :-
- Nonsurgical Extraction
If teeth are severely affected by periodontal disease, the gingival attachments can be incised and a dental elevator is used to separate tooth from the alveolus (tooth socket). This is accomplished by tearing the remaining periodontal ligament using a gentle twist and hold technique with a dental elevator. The tooth then "simply" lifts out of the alveolus. The extraction site is ALWAYS sutured closed to avoid infection and to minimize patient discomfort.
- Surgical Extraction
Surgical extraction techniques are particularly beneficial when normal healthy teeth, supernumary teeth (many photos using this link) or abnormal teeth require extraction. Teeth with fractured roots must be removed surgically or a root tip will be left in the alveolus. Some multi-rooted teeth can be severely affected by periodontal disease of a single root. The non-surgical technique will not be appropriate for such a tooth.
Surgical extraction is usually our preferred technique for most teeth. A surgical flap is created to allow access to the alveolar bone. High speed drills are used to expose the roots. Multi-rooted teeth can easily be sectioned to allow for safe tooth root removal. Dental luxators, elevators and extraction forceps may be helpful.
If difficulties arise during dental extraction, dental radiographs help diagnose and resolve these problems. After the tooth roots have been removed, the tooth alveolus (socket) is meticulously cleaned free of debris. The mucogingival flap is carefully prepared for a tension free closure. The alveolus is always sutured closed to avoid infection and to provide optimal patient comfort. A dental radiograph is taken to confirm that the entire tooth has been extracted and the alveolus is free of bone, root remnants or debris.
How Long Is The Procedure ?
The length of the procedure varies as it is dependent upon the number of teeth being extracted as well as the reason for extraction. Make sure you ask your dentist or oral surgeon prior to the procedure being performed
What Complications May Occur From Dental Extraction ?
Dental extraction can be awfully simple, however they can be very difficult as well. We provide step by step images on this website to help veterinarian collegues avoid complications.
These are some of the potential complications associated with dental extractions that have been presented to us :-
- Abnormal secondary teeth
- Discolored teeth
- Draining tracks
- Facial swelling
- Jaw fracture
- Tooth fracture
- Excessive bleeding
- Instruments fractured
- Perforation of canals, eyes or sinuses
- Inadequate healing (infection and oronasal fistulation)
For more information, medical assessment and medical quote
as email attachment to
Email : - info@wecareindia.com
Contact Center Tel. (+91) 9029304141 (10 am. To 8 pm. IST)
(Only for international patients seeking treatment in India)










